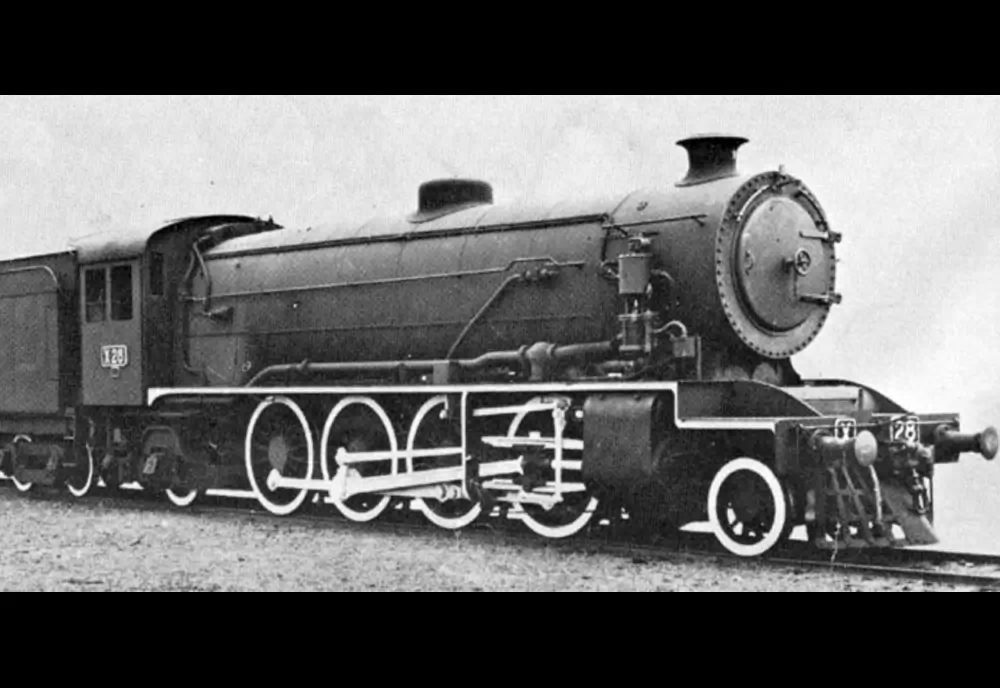
Specifications [ 2-8-2 (Mikado) ]
Baldwin Locomotive Company; American Locomotive Company (ALCO); Lima Locomotive Works - USA / Armstrong Whitworth; Kitson and Company; North British Locomotive Company; Robert and Stephensen Company; William Beardmore and Company; Vulcan Foundry - UK / Henschel and Son; Hanomag; Orenstein and Koppel - Germany / Clyde Engineering - Australia / Canadian Locomotive Company - Canada / Tampella; Lokomo - Finland \ Skoda Works - Austrian Empire
Builder
United States
Origin
1884 - 1935
Production Run
14,000 units
Production Total
Front-Right
Driver Position
19.8m | 65.0 ft
Length
NOTE: May include length of entire train set
132,450 kg
(292,052 lb | 146 US Tons)
Weight
 Steam
Power Source
Steam
Power Source
Coal-fired steam-based engine unit.
Engine / Drive Source
8 x Drive wheels (four to a frame side) with twin-wheeled leading truck and twin-wheeled trailing pair.
Traction Motor / Sets
3,300 hp
Rated Output Power
88.5 kph
(55.0 mph)
Max Speed
Wheel Arrangement
(Loco Facing Left)
Series Variants
2-8-2 - Base Series Designation (based on wheel arrangement).
"Mikado" - Adopted nickname.
"Katanga Mikado" - South African naming.